Introduction to the Angular Gyrus
The human brain is full of fascinating structures, but the angular gyrus stands out because of its role in understanding language, interpreting information, imagining concepts, and even doing math. You can think of it as a “translator hub” that turns information from different senses into meaningful ideas.
Where Is the Angular Gyrus Located?
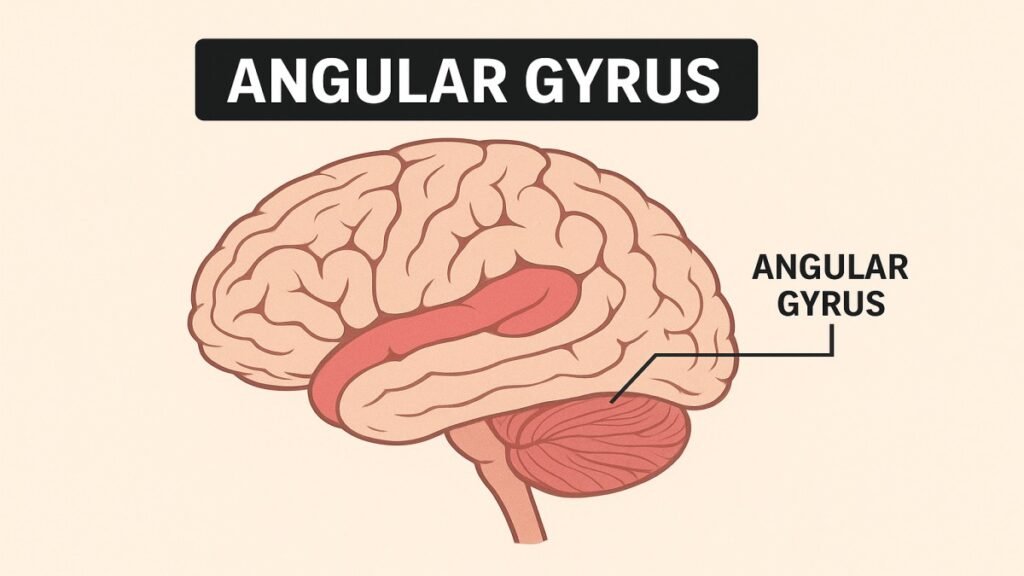
The angular gyrus lies in the posterior part of the parietal lobe, near the upper side of the temporal lobe. This location allows it to act as a bridge between sensory input and higher thinking.
Why This Small Brain Region Matters
Even though it’s small, it plays a big role in reading, writing, language comprehension, problem-solving, memory, and creativity.
Anatomy of the Angular Gyrus
Position in the Parietal Lobe
The angular gyrus sits at the intersection of the temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes — a prime spot for integrating various types of information.
Connections With Other Brain Regions
Its network connections explain why it affects so many abilities.
Communication With the Visual Cortex
It helps convert visual input (like letters or numbers) into meaningful language and concepts.
Link With Language and Memory Centers
It works closely with Wernicke’s area and the hippocampus, aiding language comprehension and memory recall.
Functions of the Angular Gyrus
Role in Language Processing
Perhaps its most famous role is in language.
Reading and Writing
It helps us decode words and sentences, turning visual symbols into meaning.
Understanding Metaphors
When someone says, “Time is a thief,” the angular gyrus helps you understand the underlying meaning rather than the literal words.
Role in Mathematics and Numbers
This region allows us to understand numerical relationships, perform mental calculations, and make sense of math concepts.
Spatial Awareness and Orientation
It helps the brain understand direction, location, and spatial relationships—essential for navigation and coordination.
Memory Retrieval and Associations
The angular gyrus helps access memories and link them with new information, supporting learning and creative thinking.
Theory of Mind and Social Cognition
It aids in understanding others’ perspectives, emotions, and intentions, which is crucial for social interaction.
The Angular Gyrus and Multisensory Integration
Combining Auditory, Visual, and Sensory Input
This brain region receives information from different senses and merges them into a unified understanding of an object or situation.
How It Helps Us Build Meaning
For example, when you see an object, hear its name, and understand its purpose, the angular gyrus helps tie everything together.
Disorders Linked to Angular Gyrus Dysfunction
Agraphia and Dyslexia
Damage can affect writing ability (agraphia) or the ability to recognize written words (dyslexia).
Gerstmann Syndrome
A rare condition involving:
- Finger recognition problems
- Right-left confusion
- Difficulty writing
- Trouble with basic math
Semantic Processing Disorders
People may struggle to understand meanings, symbols, or abstract concepts.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
These include:
- Difficulty reading or writing
- Trouble with calculations
- Understanding metaphors
- Memory recall problems
Angular Gyrus in Modern Neuroscience
Brain Imaging Insights
Modern MRI and fMRI studies show that the angular gyrus lights up when you imagine concepts, read, do math, or think creatively.
Cognitive Science Discoveries
Researchers believe the angular gyrus is essential for imagination, empathy, and complex problem-solving.
How to Protect and Support Cognitive Health
Brain-Healthy Activities
- Reading and writing regularly
- Learning new languages
- Solving puzzles
- Practicing creative skills
Nutrition and Lifestyle Choices
- Omega-3–rich foods
- Adequate sleep
- Stress reduction
- Physical activity
These habits support overall brain function, including the angular gyrus.
Conclusion
The angular gyrus may be small, but its influence on human cognition is enormous. From language and math to memory and creativity, it’s a powerhouse that shapes how we understand the world. Supporting your brain health can help keep this vital region functioning at its best.
FAQs
1. What is the main function of the angular gyrus?
It integrates sensory information and helps with language, memory, and reasoning.
2. What happens if the angular gyrus is damaged?
It may cause difficulties in reading, writing, math, or understanding concepts.
3. Is the angular gyrus involved in creativity?
Yes, it plays a major role in imagination and forming abstract ideas.
4. Can the angular gyrus improve with training?
Activities like reading, learning languages, and solving puzzles can strengthen cognitive pathways.
5. Is the angular gyrus the same as Wernicke’s area?
No, but they work closely together in language comprehension.