Introduction
What Is Brassica?
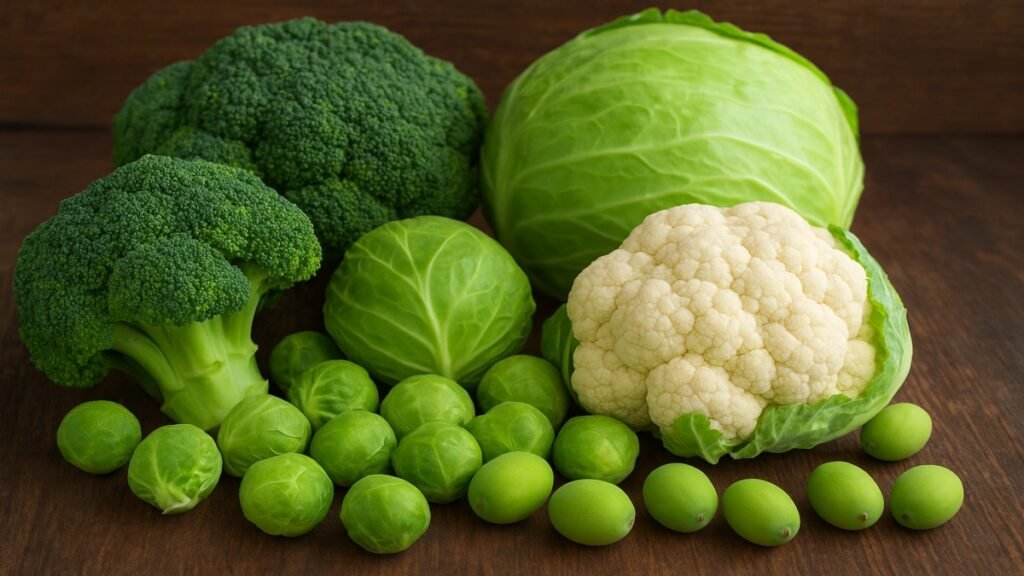
Brassica refers to a large group of vegetables belonging to the Brassicaceae family, popularly known as cruciferous vegetables. This family includes well-known favorites like broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, kale, and mustard greens. These veggies are packed with nutrients and known for their slightly peppery flavor.
Why Brassica Vegetables Are So Popular
From health-conscious eaters to gourmet chefs, brassica veggies have become dietary staples around the world. They’re incredibly versatile—you can steam them, roast them, stir-fry them, or even eat some varieties raw. Plus, they offer powerful health benefits, making them a true superfood group.
Major Types of Brassica Vegetables
Leafy Brassicas
These include kale, collard greens, mustard greens, and cabbage. They’re rich in vitamins A, C, and K.
Flowering Brassicas
Broccoli, cauliflower, and Romanesco fall into this category. They are known for their unique textures and mild flavors.
Root Brassicas
Turnips, radishes, and rutabagas belong here. They offer both edible roots and leafy tops.
Stem Brassicas
Vegetables like kohlrabi are grown for their tender, bulb-like stems.
Nutritional Value of Brassica Vegetables
Vitamins
Brassicas provide a wealth of vitamins including:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin A
- Folate
These vitamins support immunity, bone health, and cell repair.
Minerals
Minerals like potassium, calcium, and magnesium are present in significant amounts, making brassicas effective for heart and muscle health.
Fiber and Antioxidants
These veggies are rich in fiber, helping digestion and weight control. They also contain antioxidants like sulforaphane, which support detoxification and disease prevention.
Health Benefits of Brassica
Supports Immune System
High vitamin C levels help boost immunity and fight off infections.
Promotes Heart Health
Fiber, antioxidants, and potassium contribute to lower cholesterol and healthy blood pressure.
Helps with Detoxification
Compounds like glucosinolates help the liver remove toxins, keeping the body clean and balanced.
Aids in Weight Management
Low in calories yet high in fiber, brassicas keep you full longer without adding excess calories.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Their antioxidants help reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Supports Digestive Health
Fiber improves bowel movement regularity and feeds healthy gut bacteria.
Culinary Uses of Brassica Vegetables
Raw Preparations
Some brassicas, like cabbage and kale, can be enjoyed raw in salads, slaws, and smoothies.
Cooked Dishes
Roasting, steaming, and stir-frying bring out their natural sweetness. Cauliflower can even be made into “rice” or “pizza crust.”
Fermented Foods
Brassicas are perfect for fermentation. Sauerkraut and kimchi are well-loved traditional dishes packed with probiotics.
How to Select and Store Brassica
Choosing Fresh Vegetables
Look for:
- Firmness
- Bright color
- No wilting or brown spots
Proper Storage Tips
Store leafy greens in the fridge, wrapped loosely. Root brassicas can last longer in cool, dark places. Cauliflower and broccoli stay fresh when refrigerated in breathable bags.
Potential Side Effects
Digestive Discomfort
Some people may experience gas or bloating due to high fiber and sulfur content.
Thyroid Considerations
Raw brassicas contain goitrogens, which may interfere with thyroid function in sensitive individuals. Cooking reduces these effects significantly.
Tips for Adding Brassica to Your Diet
Easy Recipes
- Stir-fried broccoli with garlic
- Kale smoothies
- Roasted Brussels sprouts
- Cauliflower soup
Daily Recommended Intake
Aim for at least 1–2 cups of brassicas per day to enjoy their full health benefits.
Conclusion
Brassica vegetables are nutrient-rich, versatile, and incredibly beneficial for your health. Whether you enjoy them raw, roasted, or fermented, adding them to your diet can boost immunity, support digestion, protect the heart, and promote overall wellness. These vegetables truly deserve their reputation as superfoods.
FAQs
1. What vegetables are part of the brassica family?
Broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, kale, radish, mustard greens, and turnips are common examples.
2. Are brassica vegetables good for weight loss?
Yes, their low calorie and high fiber content make them excellent for weight management.
3. Can brassica vegetables cause bloating?
Some individuals may experience gas or bloating due to their fiber and sulfur content.
4. Do brassicas need to be cooked to be healthy?
No, both raw and cooked brassicas offer health benefits. Cooking can reduce goitrogens, though.
5. Which brassica vegetable is the healthiest?
All brassicas are nutritious, but kale and broccoli are often considered the most nutrient-dense.