Introduction to Endometrial Polyps
What Is an Endometrial Polyp?
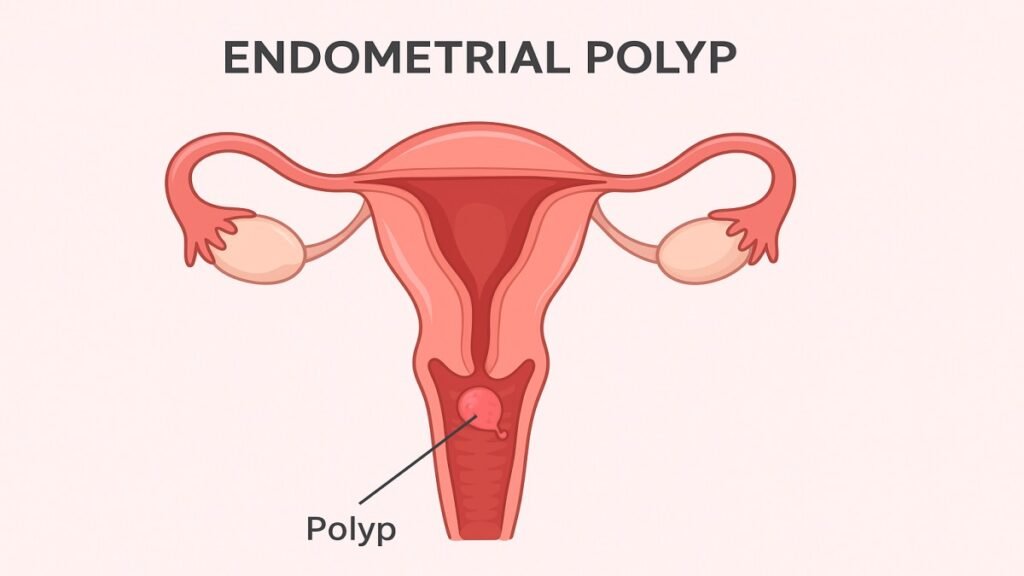
An endometrial polyp is a small, soft, noncancerous growth that forms inside the uterus from an overgrowth of the endometrial tissue. Think of it like a tiny skin tag but located within the uterine lining. These growths range from a few millimeters to several centimeters and can occur singly or in clusters.
How Common Are Endometrial Polyps?
They’re surprisingly common especially in women aged 40–55. Many women never know they have one unless symptoms appear or a doctor finds it during a routine exam.
Anatomy and Function of the Endometrium
Role of the Uterine Lining
The endometrium thickens and sheds during each menstrual cycle. Its main job is to create a healthy environment for a potential pregnancy.
Why Tissue Overgrowth Occurs
Hormonal changes, especially estrogen levels, can cause the lining to grow excessively, leading to the formation of a polyp.
Causes of Endometrial Polyps
Hormonal Imbalance
Estrogen overstimulation is the biggest culprit. When estrogen levels stay high without sufficient progesterone to balance it, tissue overgrowth occurs.
Age and Reproductive Factors
Polyps develop more frequently during perimenopause when hormones fluctuate widely.
Lifestyle and Medical Conditions
Conditions like obesity or metabolic issues increase estrogen levels, encouraging polyp growth.
Medication-Related Causes
Certain medications, such as tamoxifen used in breast cancer treatment, may stimulate endometrial tissue.
Risk Factors
Obesity
Fat tissue produces estrogen, which can increase the likelihood of polyp formation.
Hypertension
Chronic high blood pressure has been linked to the development of various uterine abnormalities.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Women with PCOS experience hormonal imbalance, creating an environment where polyps are more likely.
Menopause and Perimenopause
Fluctuating hormones make this age group the most vulnerable.
Signs and Symptoms
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
This includes:
- Bleeding between periods
- Heavy menstrual periods
- Postmenopausal bleeding
Infertility or Difficulty Conceiving
Polyps can interfere with embryo implantation, making conception harder.
Pelvic Discomfort
Some women may feel cramping or pelvic pressure.
When Polyps Are Silent
Many women have no symptoms at all and learn about polyps during imaging tests.
How Endometrial Polyps Are Diagnosed
Ultrasound Examination
A transvaginal ultrasound can often detect abnormal thickening or growths inside the uterus.
Hysteroscopy
A small camera is inserted into the uterus, allowing doctors to view and remove polyps in real time.
Biopsy and Pathology
A biopsy confirms whether the growth is benign, precancerous, or rarely cancerous.
Differential Diagnosis
Doctors must rule out fibroids, hyperplasia, and other uterine conditions.
Are Endometrial Polyps Dangerous?
Benign vs. Precancerous Growths
Most polyps are harmless. However, a small percentage may show precancerous changes.
Cancer Risk Factors
Higher cancer risk occurs in postmenopausal women, those with obesity, and women taking certain medications.
Treatment Options
Watchful Waiting
If the polyp is small and symptom-free, monitoring may be enough.
Medications
Hormonal medications may temporarily reduce symptoms, but polyps often return once treatment stops.
Polypectomy
This minor procedure removes the polyp using hysteroscopy. It’s quick, effective, and often done on an outpatient basis.
Post-Treatment Care
Regular follow-ups ensure polyps don’t grow back and help monitor hormonal balance.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
Hormonal Balance
Maintaining stable hormone levels through diet, exercise, and managing stress is key.
Weight Management
Healthy weight reduces estrogen production from fat tissue.
Routine Screenings
Regular gynecological checkups can help detect polyps early.
Living With Endometrial Polyps
Fertility Considerations
Removing polyps can significantly improve fertility outcomes for many women.
Emotional and Mental Well-Being
Dealing with unexpected symptoms or infertility can be stressful. Support groups, therapy, or counseling can be helpful.
Conclusion
Endometrial polyps are common, treatable, and usually not dangerous. Understanding what causes them, how they’re diagnosed, and what treatment options exist empowers you to take control of your reproductive health. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or simply want to stay informed, early detection and lifestyle awareness make all the difference.
FAQs
1. Can endometrial polyps go away on their own?
Yes, small polyps can sometimes shrink or disappear, especially in premenopausal women. However, many require removal.
2. Are endometrial polyps the same as fibroids?
No. Polyps are soft tissue overgrowths, while fibroids are muscular tumors.
3. Do polyps always cause heavy bleeding?
Not always. Many polyps cause no symptoms at all.
4. Can endometrial polyps return after removal?
Yes, recurrence is possible, especially in women with hormonal imbalance.
5. Is polyp removal painful?
Most women experience minimal pain, and the procedure is typically done under mild anesthesia.